What is the Rule Book?
The rulebook allows the creation of rules that define which shipping solution and/or extra option to use for each type of shipping that comes from an online shop or CSV import
In the case of Open Source shops (e.g. woocommerce) the use of the rulebook is important for shops that are already set up and where there are no intentions to change shipping methods. They are also important for shops where there is only one shipping method configured (e.g. free shipping) but there is interest in using several shipping solutions and/or extra options depending on the shipping type
In Closed Source shops (e.g. Shopify) the use of the rulebook is more important because it’s the only way that allows the differential assignment of several shipping solutions and/or extra options to the existing shipping methods in the shop.
It is important to note that shipping methods (shipping description and shipping value presented to the customer at check out) are configured in the online shop. The rulebook assigns the desired shipping solution and/or extra options to each of these methods.
The fundamental principles for using the rule book are:
- Rules created in the rule book are cumulative so the order in which they are stored is important.
- You should pay special attention if there are conflicting rules. In this case you can add more shipping characteristics to make the rules unique or use the Stop Processing condition to prevent one rule overlapping with another.
- Rules are based on one or more characteristics of the shipment. Rules can be created where all selected characteristics must be present (All) or only some (Any);
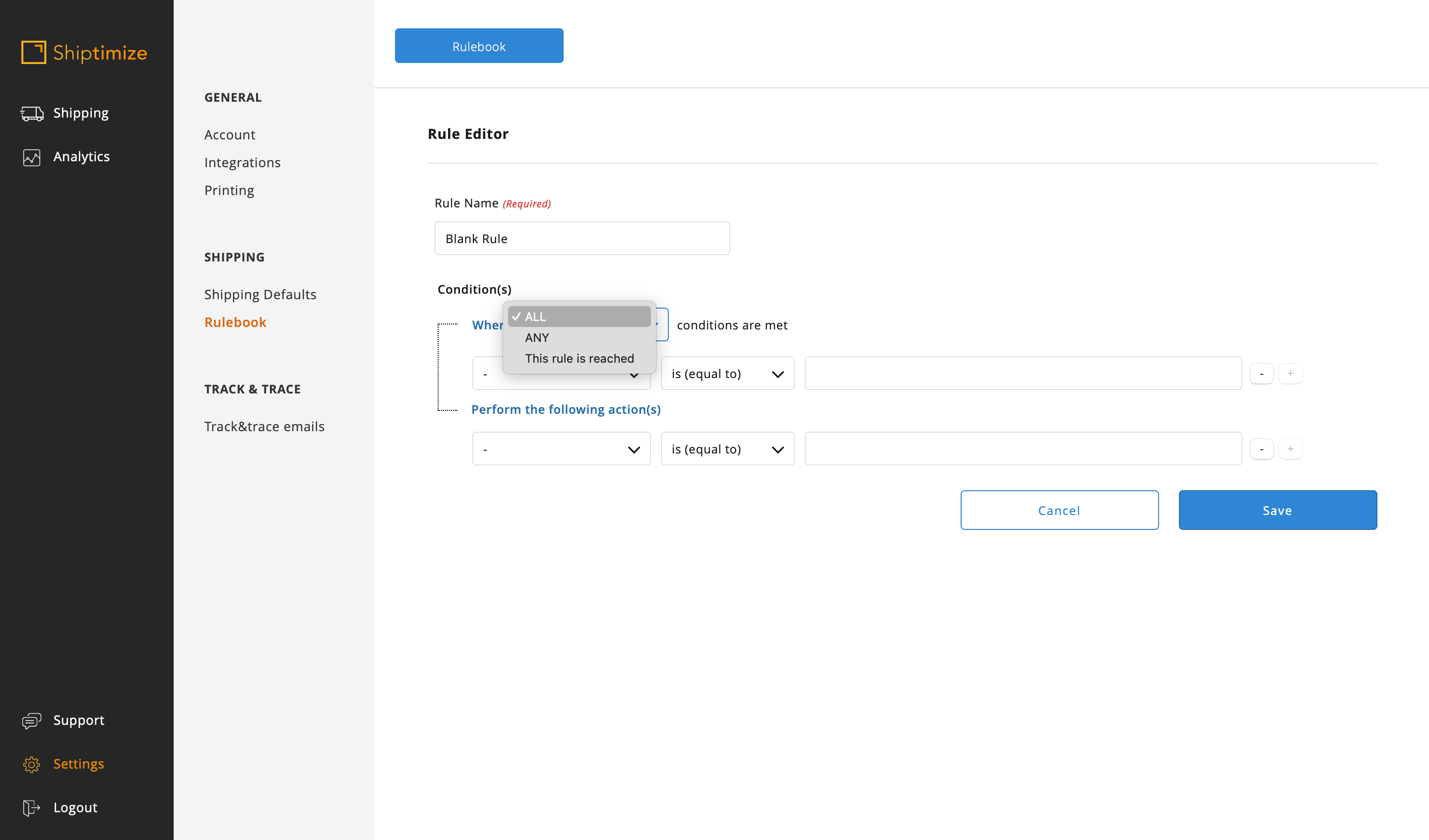
A condition can be selected about the selected characteristic (the most frequent are the conditions “equal”, “not equal”, “contains” and “does not contain”)
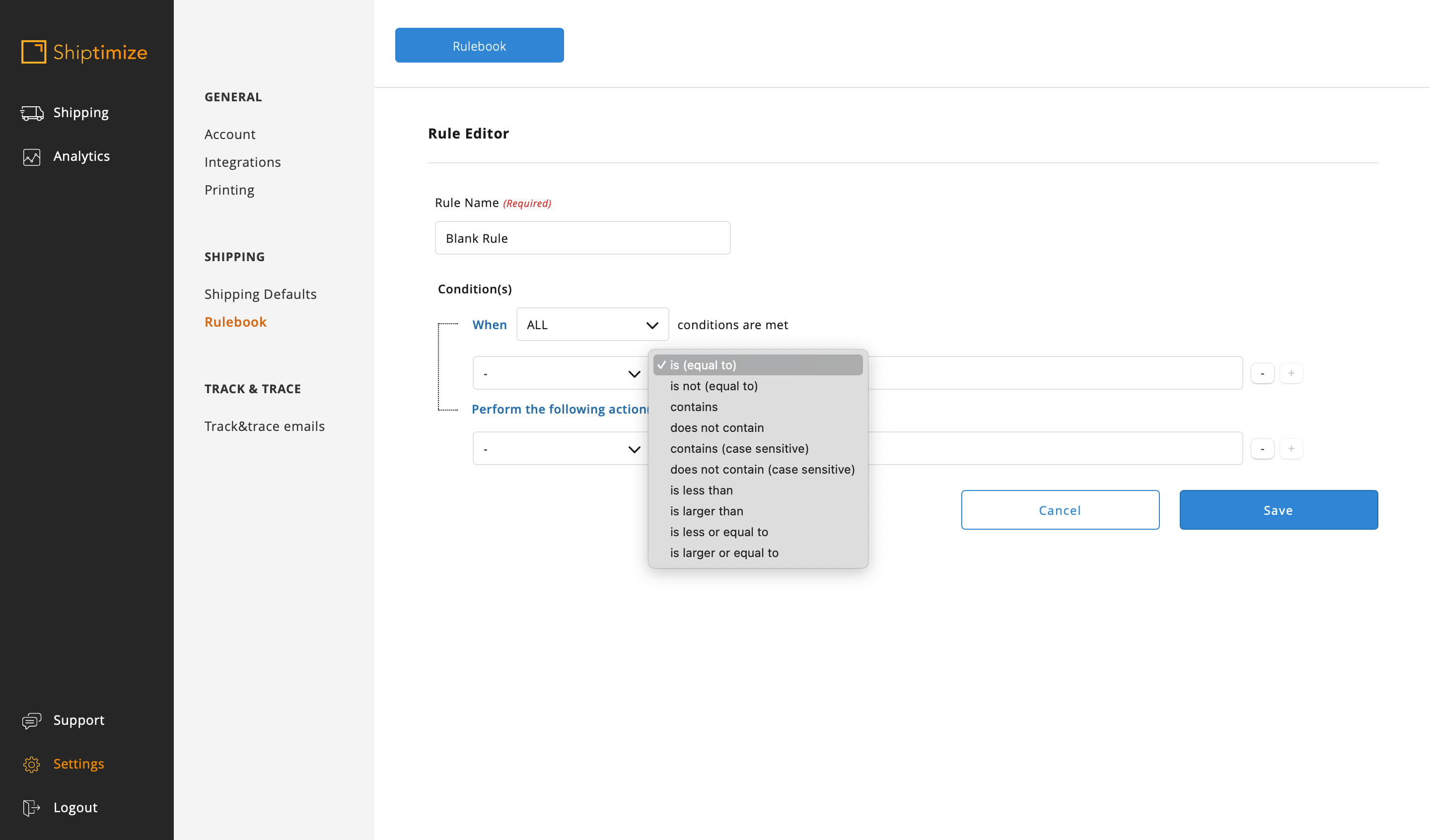
And an action can be selected to apply when the conditions for that feature are present
(the most common is Carrier / Extra Option that allows to choose the shipping solution and Extra Option to apply, Stop processing rules that is important in case of conflicting rules and Do not store shipment that is used when shipping should not be imported (e.g. Store pickup))
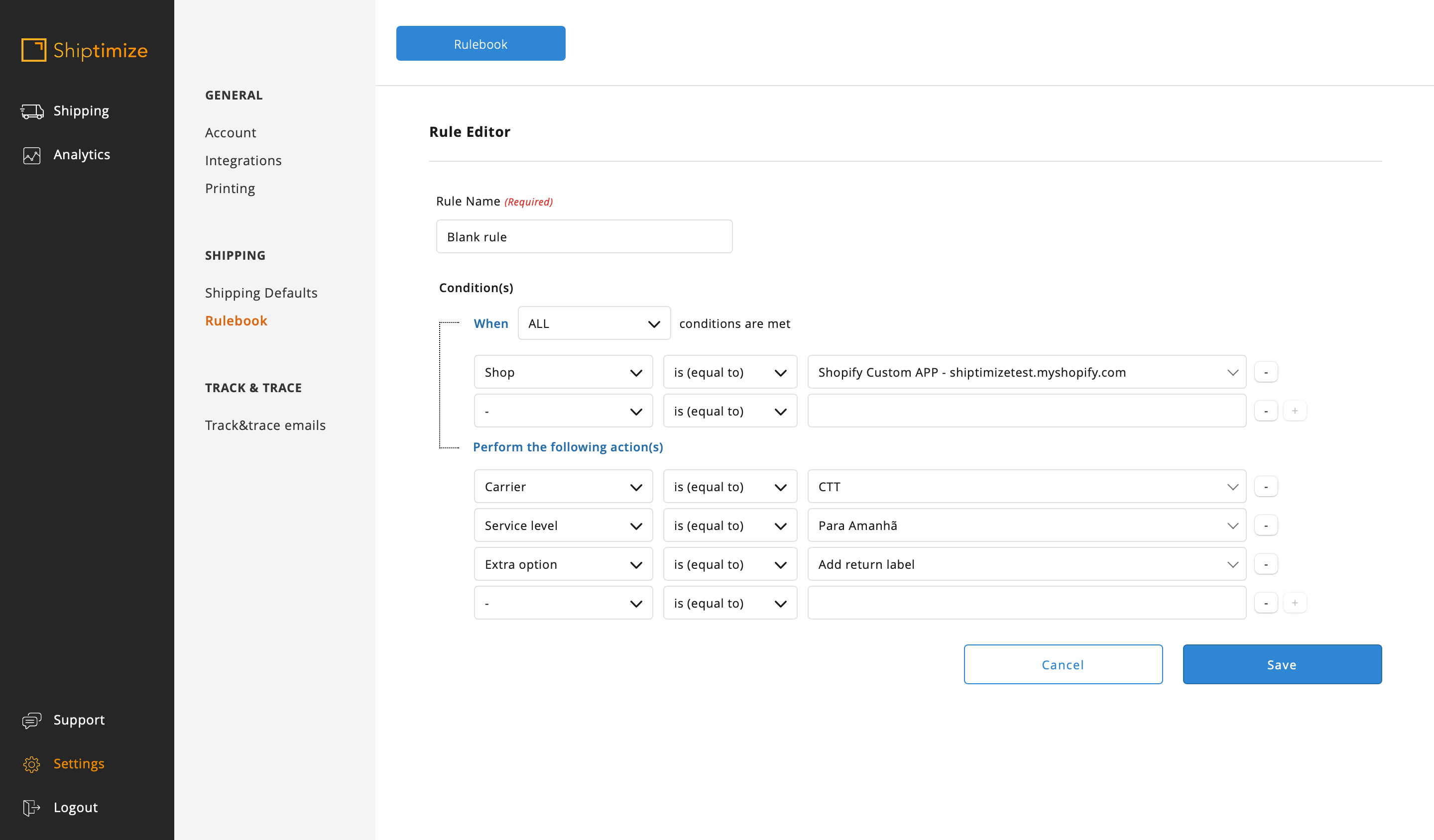
Closed Source example rules
In the case of closed source shops the configuration of shipping rules depends on the shop configuration, i.e., if the shop has more than one shipping method and the intention of using more than one shipping solution and/or extra options.
Only one shipping method and the intention of using only one shipping solution and/or extra options
In this case you can create a simple shipping rule where the selected characteristic is the Shop, the condition is the same as the shop name and the shipping solution and/or extra options are the ones you want.
Presence of several shipping methods in the shop and want to use several shipping solutions / extra options
In this case there are two options to assign a rule to the different shipping methods:
- Creating a rule for each shipping method: As many rules are created as there are shipping methods in the shop. This option is practical for those who use flat rates in the online shop, i.e., the shipping value was not confirmed either by weight or by shopping cart value.
When creating this simple rule, the selected characteristics are “Shop” and “Shipping method” and the condition is “equal”. The list of shipping methods available in the shop will appear and you must select the desired method.
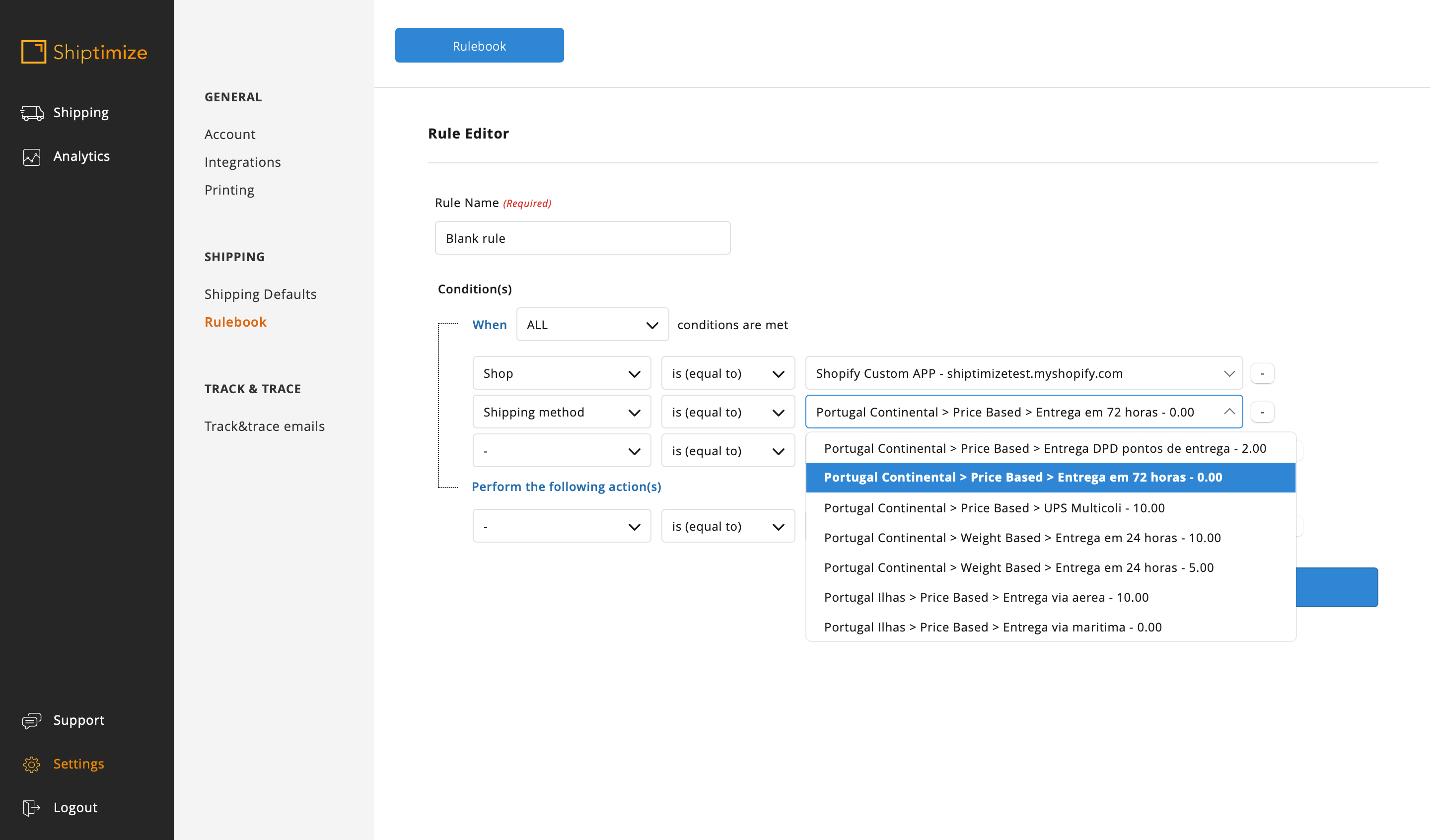
In the action you must select the Carrier, Service level and the extra option if desired.
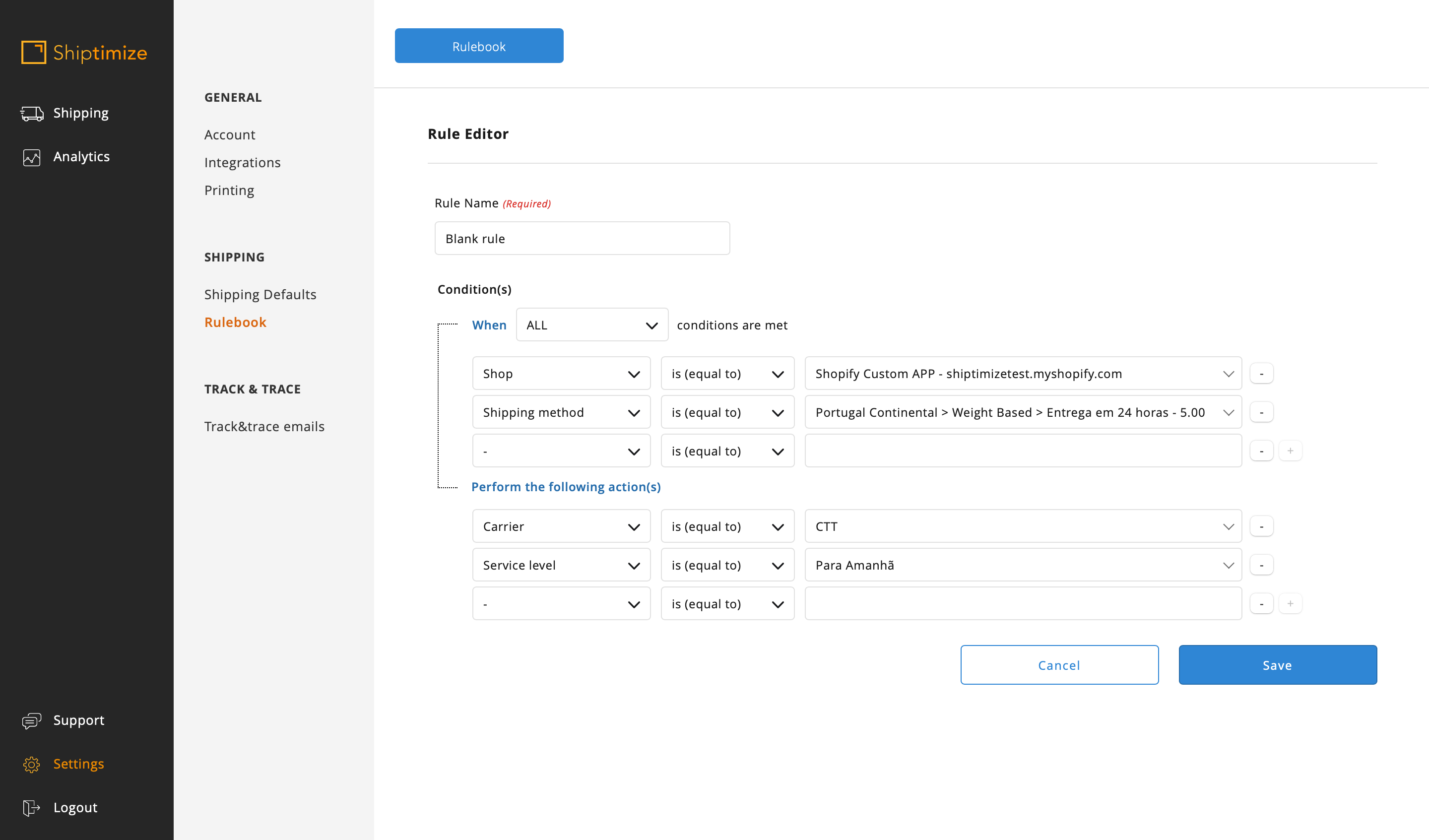
You must repeat this rule for all existing shipping methods
- Creating shipping rules that aggregate several shipping methods In this case, each rule will include several shipping methods, which reduces the number of rules to create, making it easier to manage. This option is very important in the case of shops where the configuration of shipping methods was made using rules of weight or value of the shopping cart.
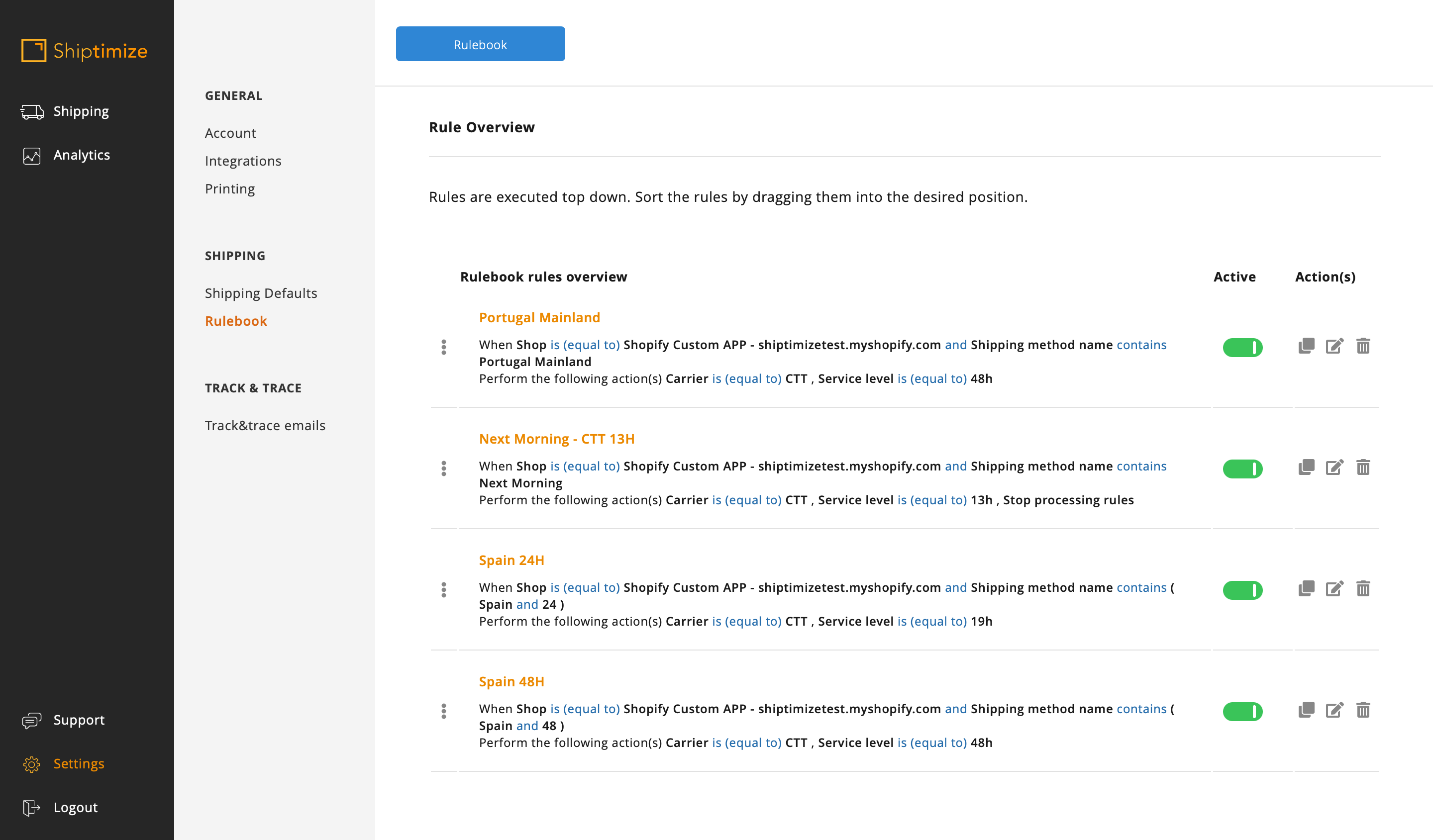
The most accessible way to create these rules is the shipping method name as characteristics and the condition “Contains” or “Does not contain” parts or the totality of the shipping name for the distinction between the rules (e.g. In the case of having several shipping methods for Portugal Mainland differentiating only in the weight of the shopping cart it’s possible to use the condition Contains Portugal Mainland for the rule creation)
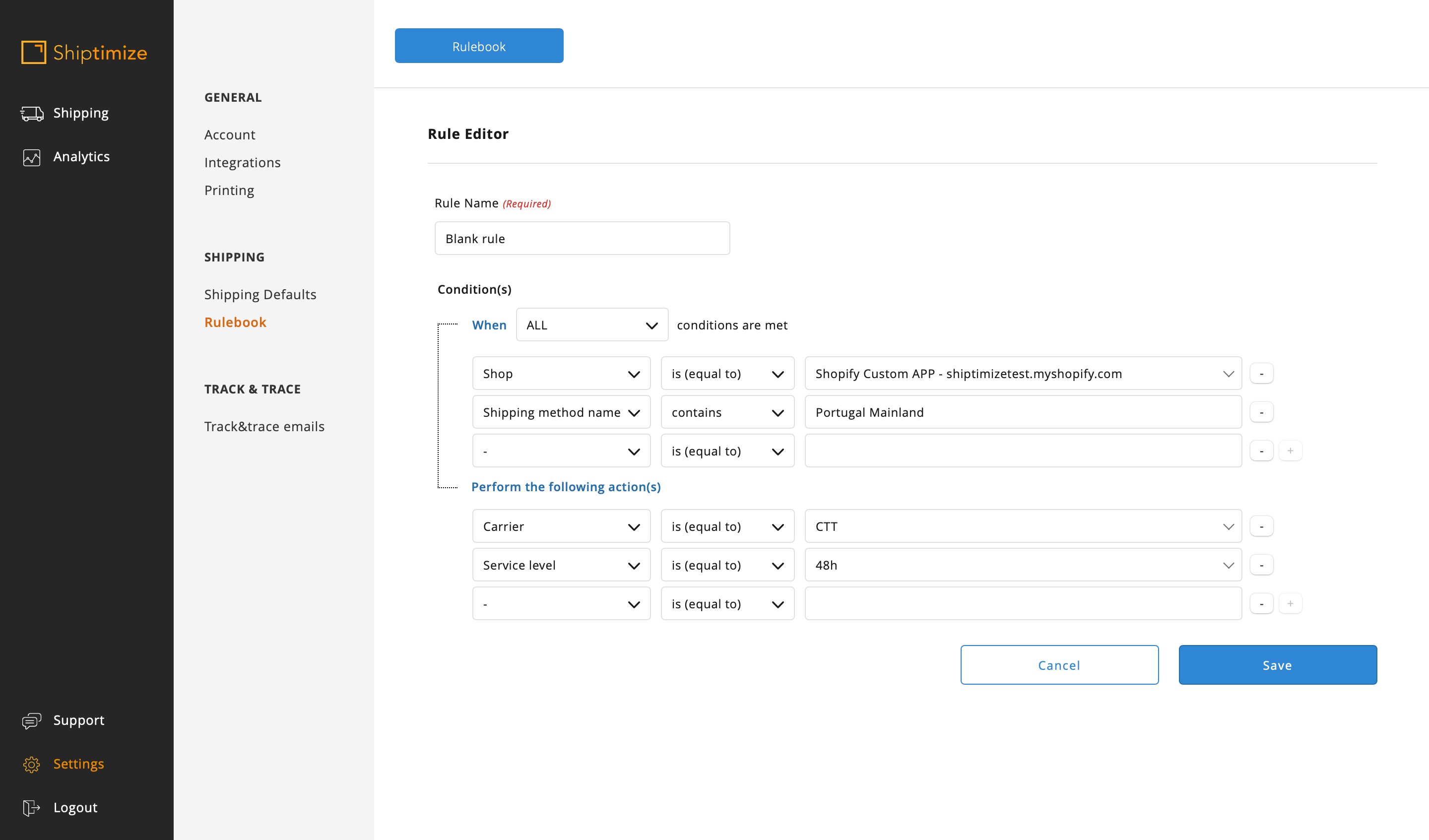
In this example as there are methods which contain Portugal Mainland but which correspond to two different shipping solutions more than one condition should be added to the rule or a second rule should be added in parallel.
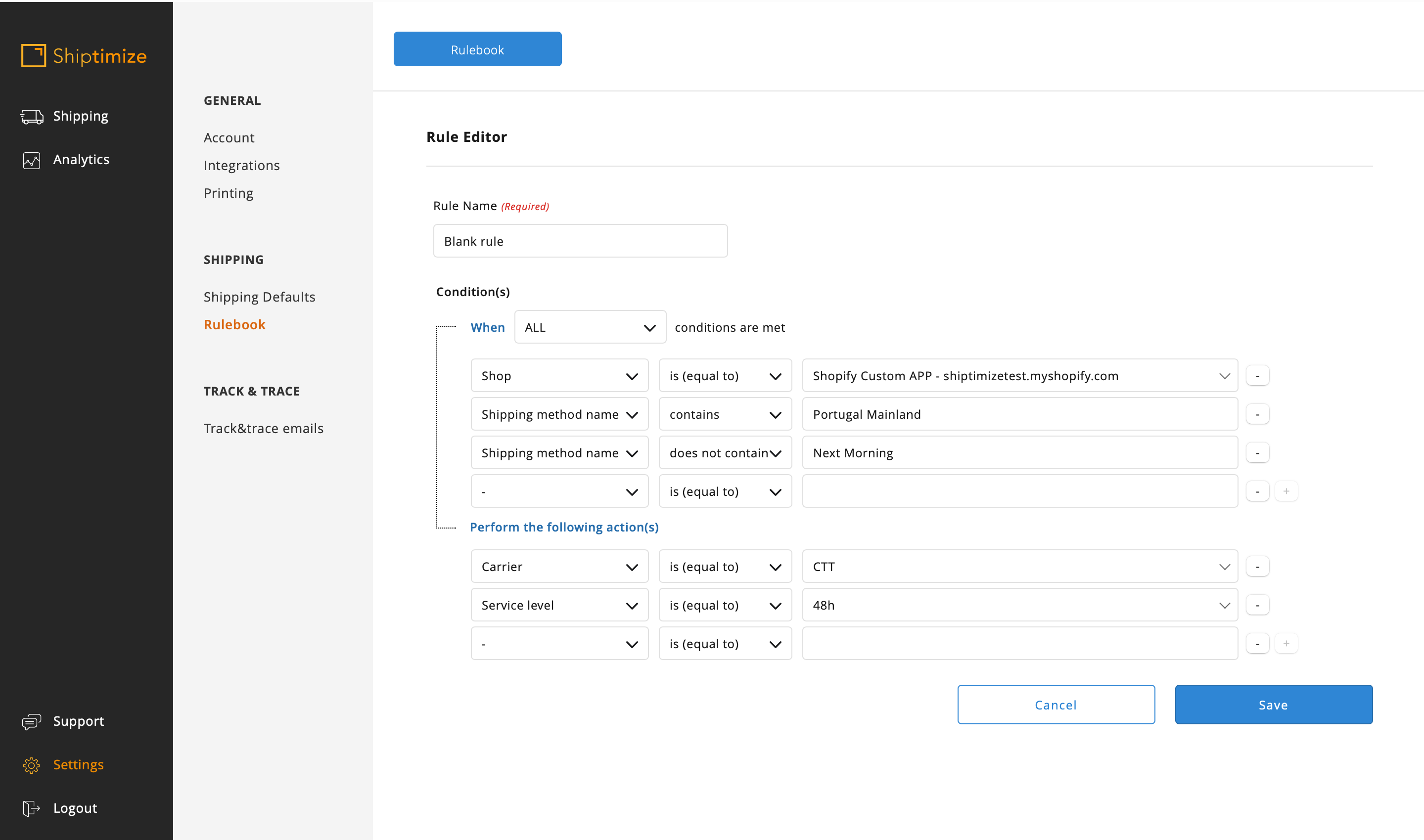
Or
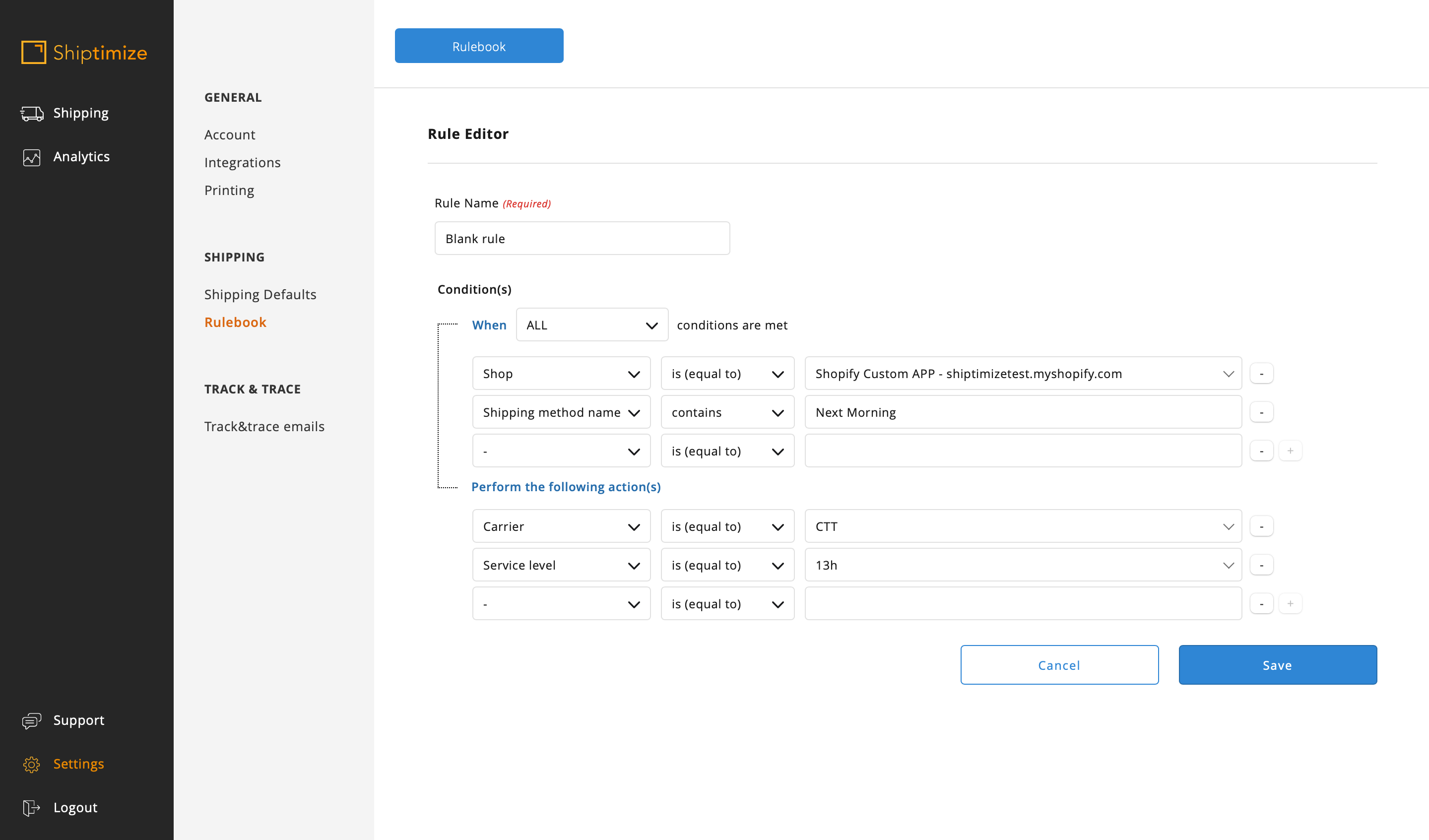
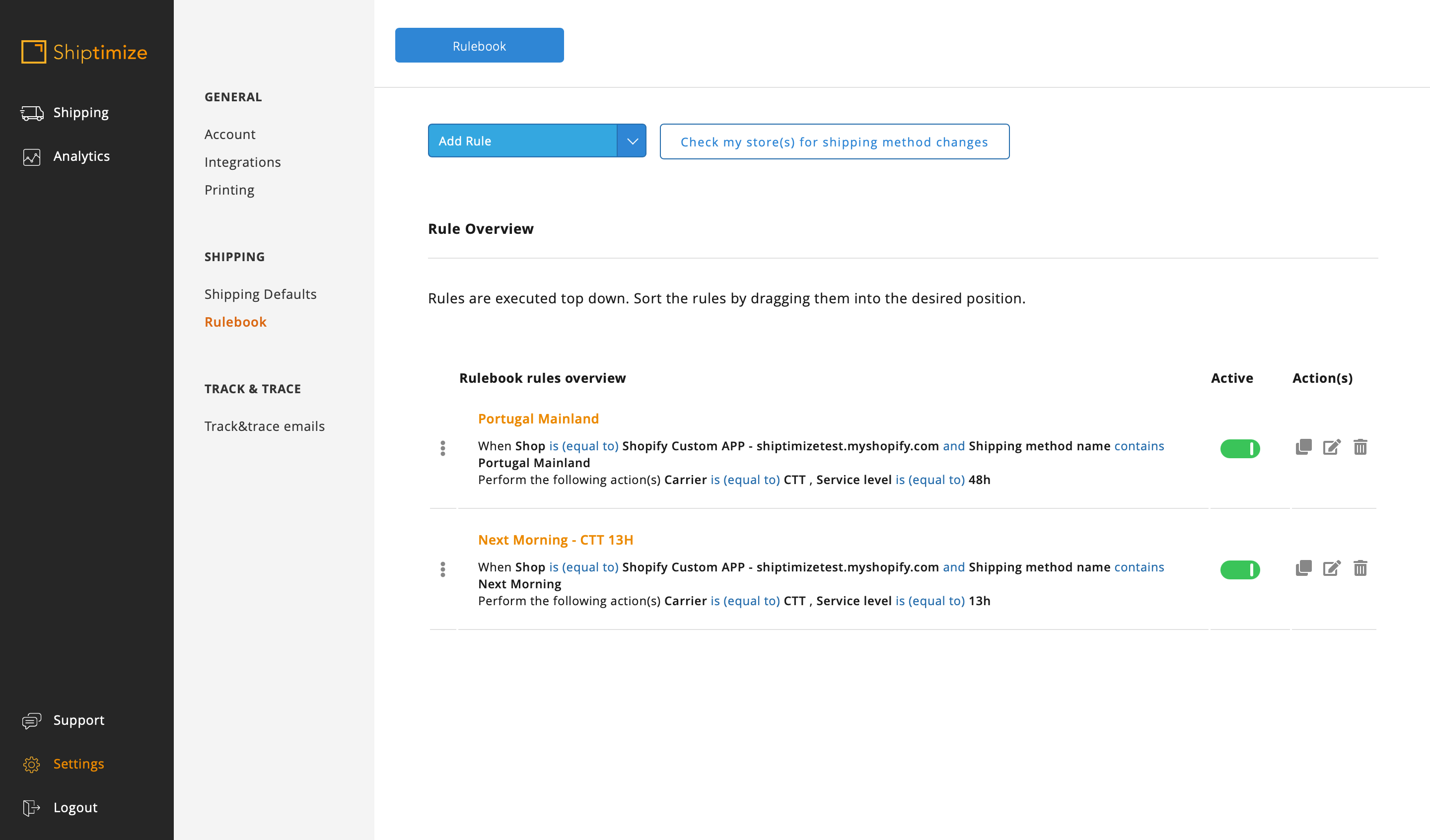
In this second option it is important that the rules are in the correct order or else there would be a need to add the stop processing action.
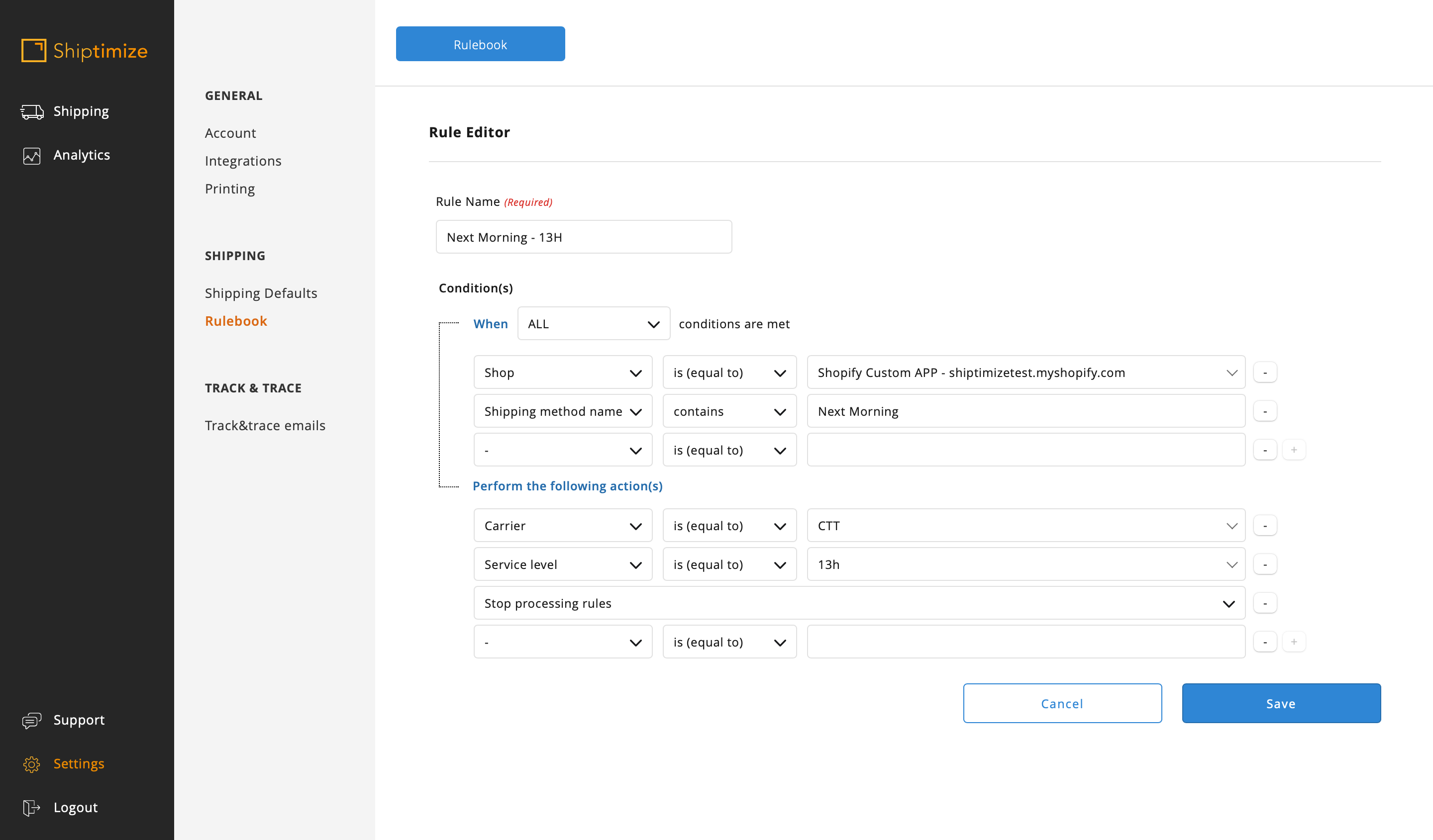
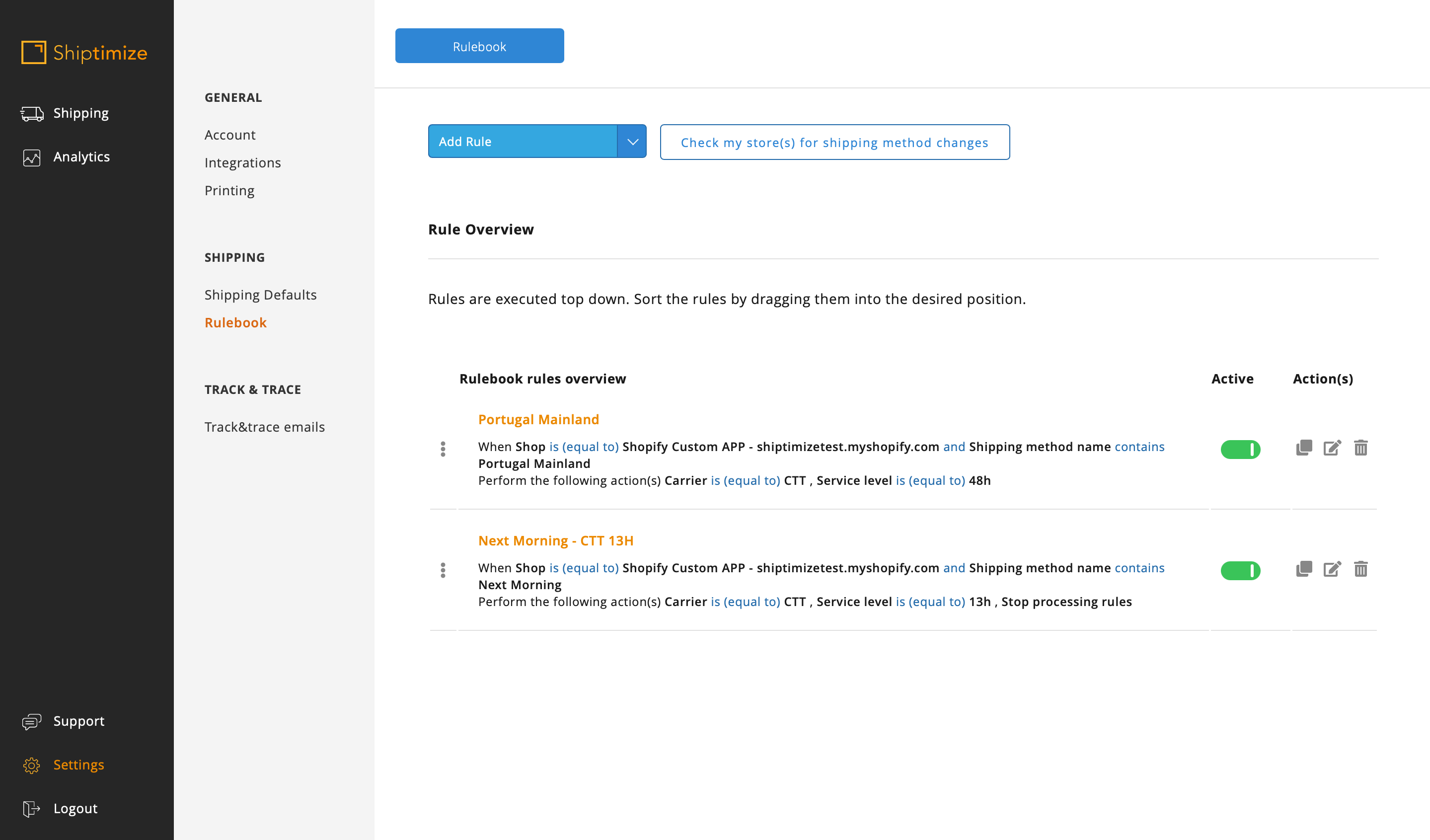
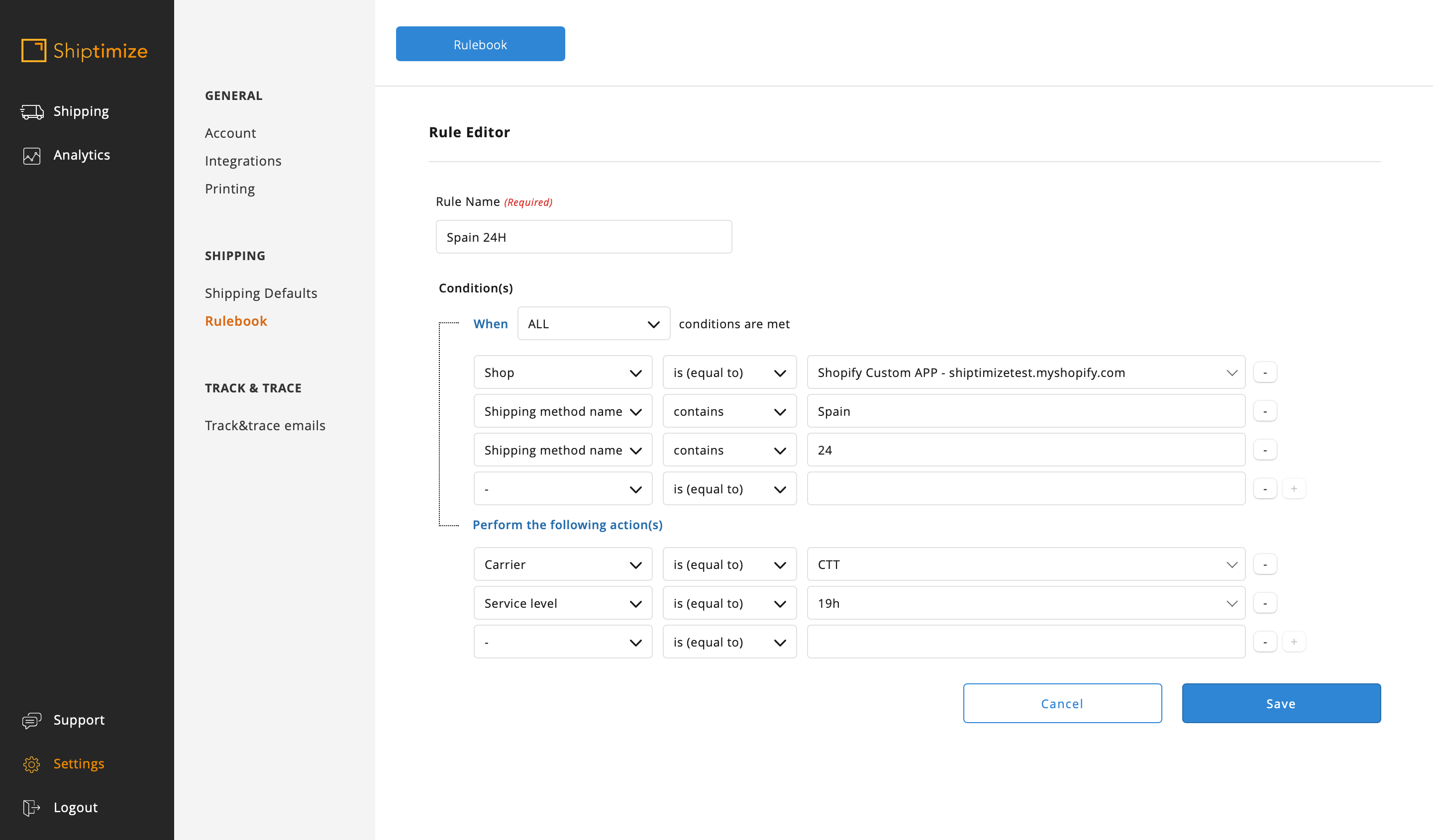
If there are different shipping methods that differ in parts of the name you can use several conditions in the same rule. In this example there was the shipping method CTT Spain – Delivery in 24 Hours and the method CTT Spain – Delivery in 48 Hours so Spain was used to differentiate from the other rules and the 24 and 48 to distinguish between them.
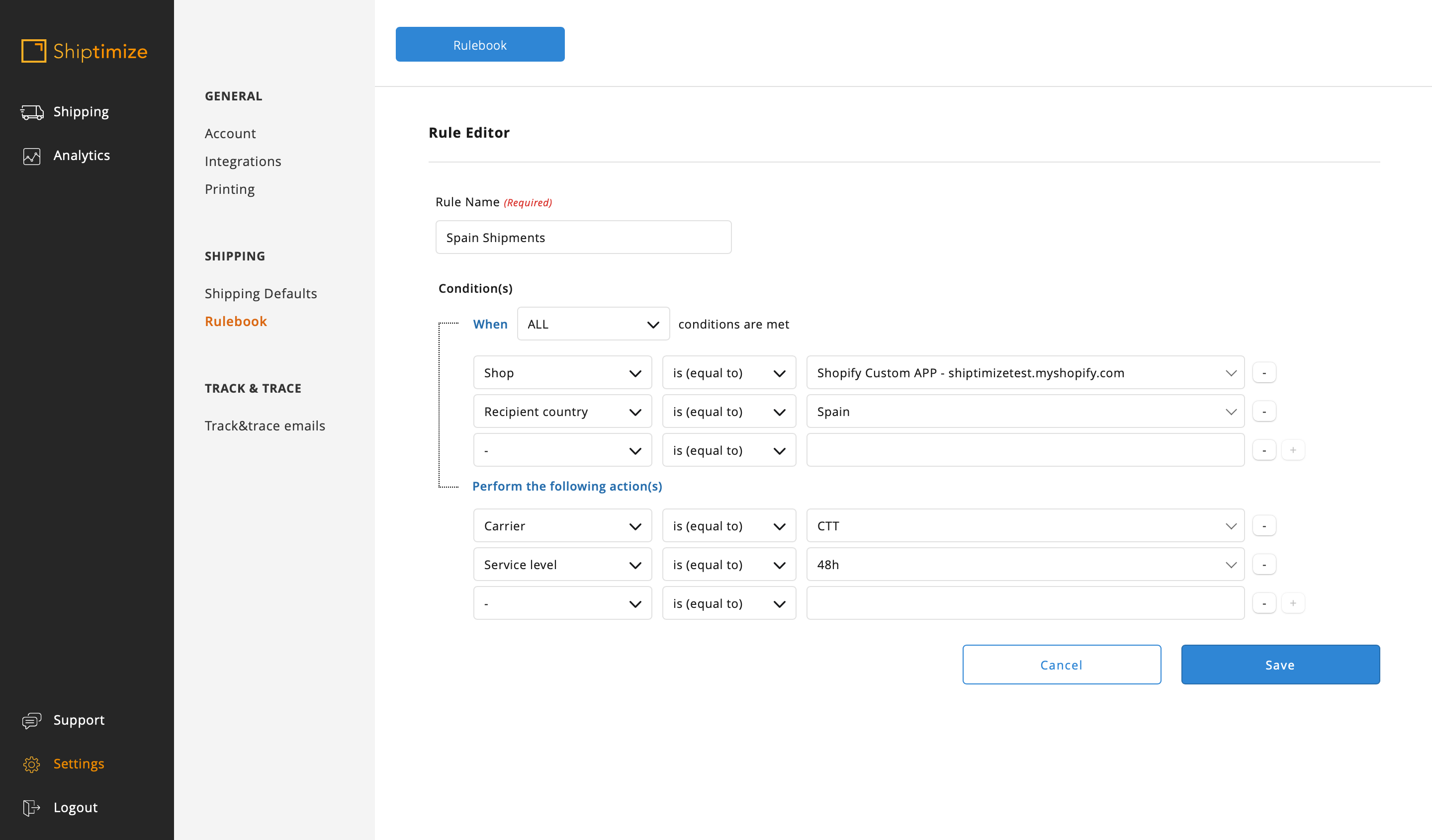
Presence of a single shipping method in the shop, but want to use several shipping solutions / extra options
In this case you must use characteristics of the items that are not the name of the shipping method to distinguish the various rules as for example the Country and / or Zone of the Country of the recipient. You can also use the weight or other condition that you might find advantageous.
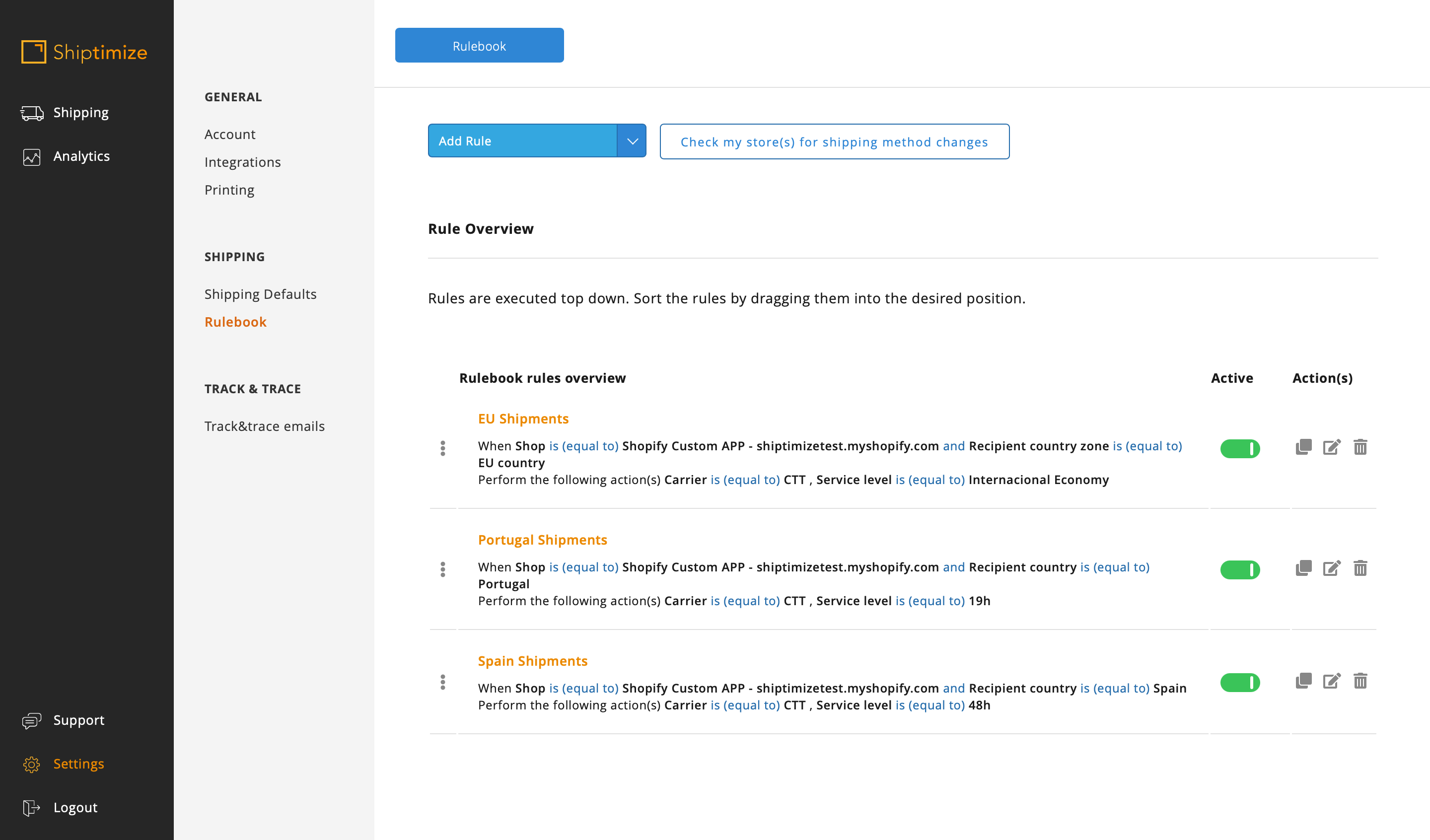
In our example the shop used only one shipping method Free for the EU but we intend that the shipments to Portugal are made with the shipping solution 19H, to Spain 48H and for the rest of the EU with the solution International Economic. So, since the rules will be conflicting (Portugal and Spain belong to the EU) we have to create 3 rules in the correct order (first for EU shipments and the second and third for Portugal and Spain)
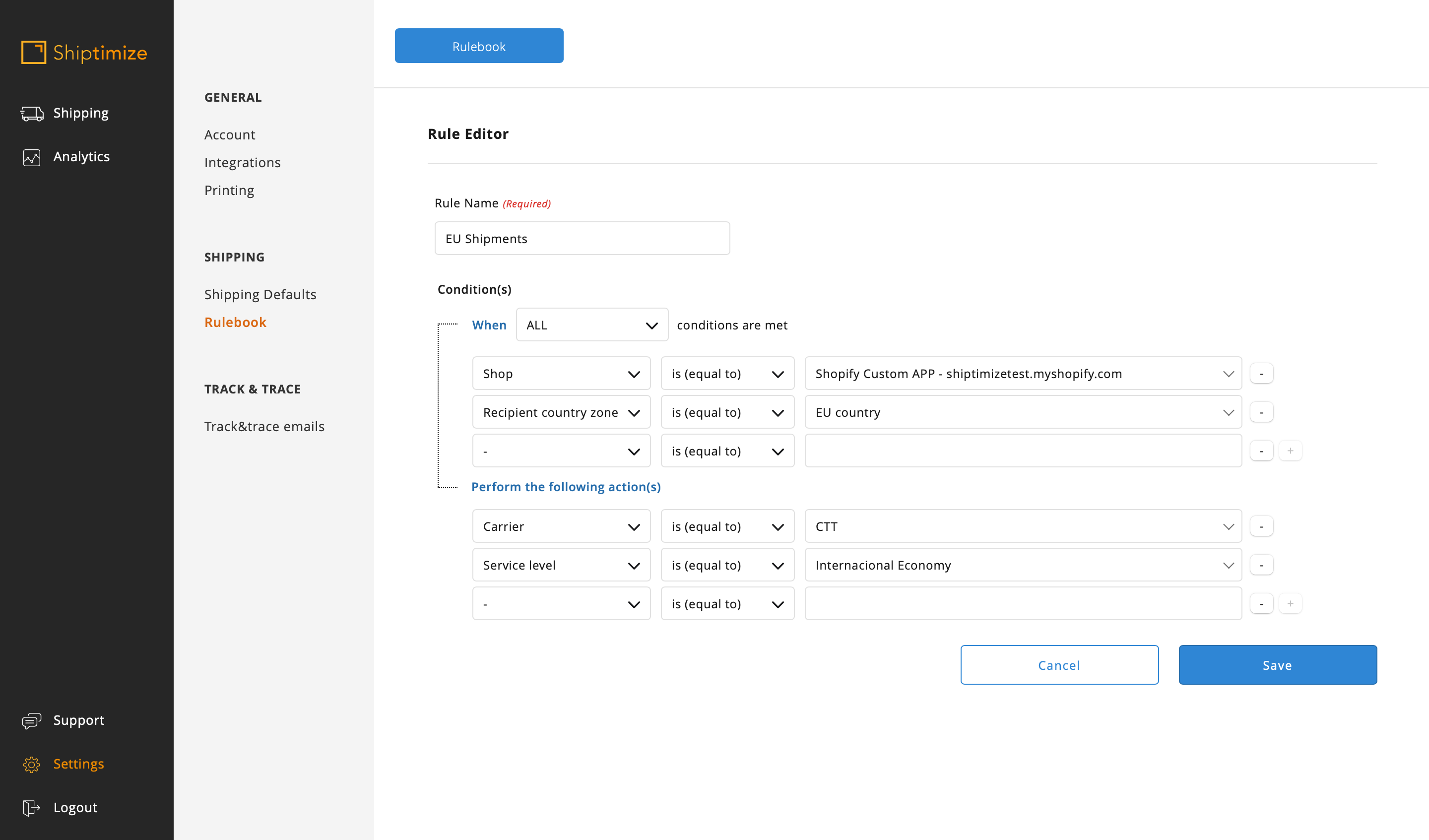
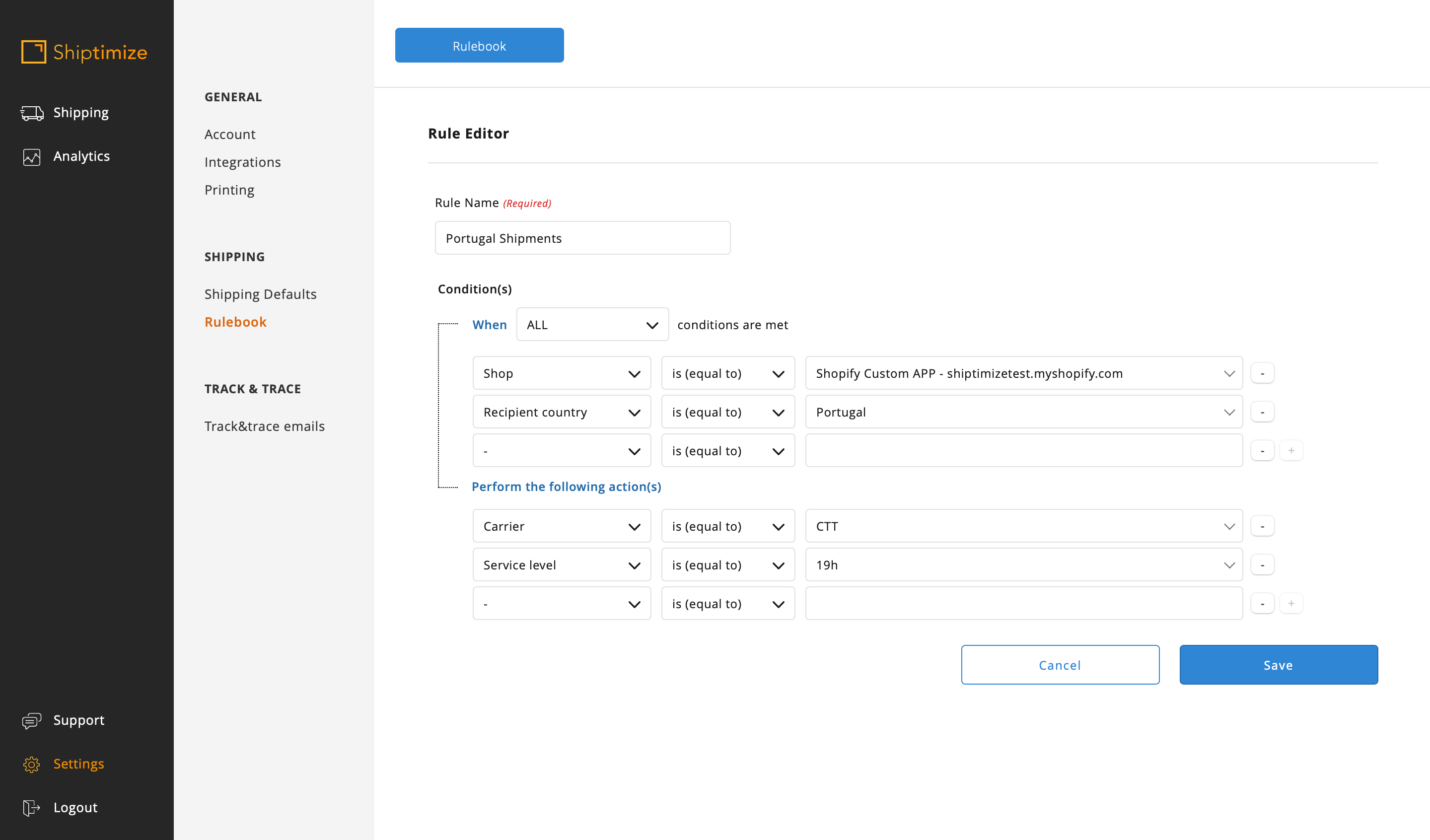
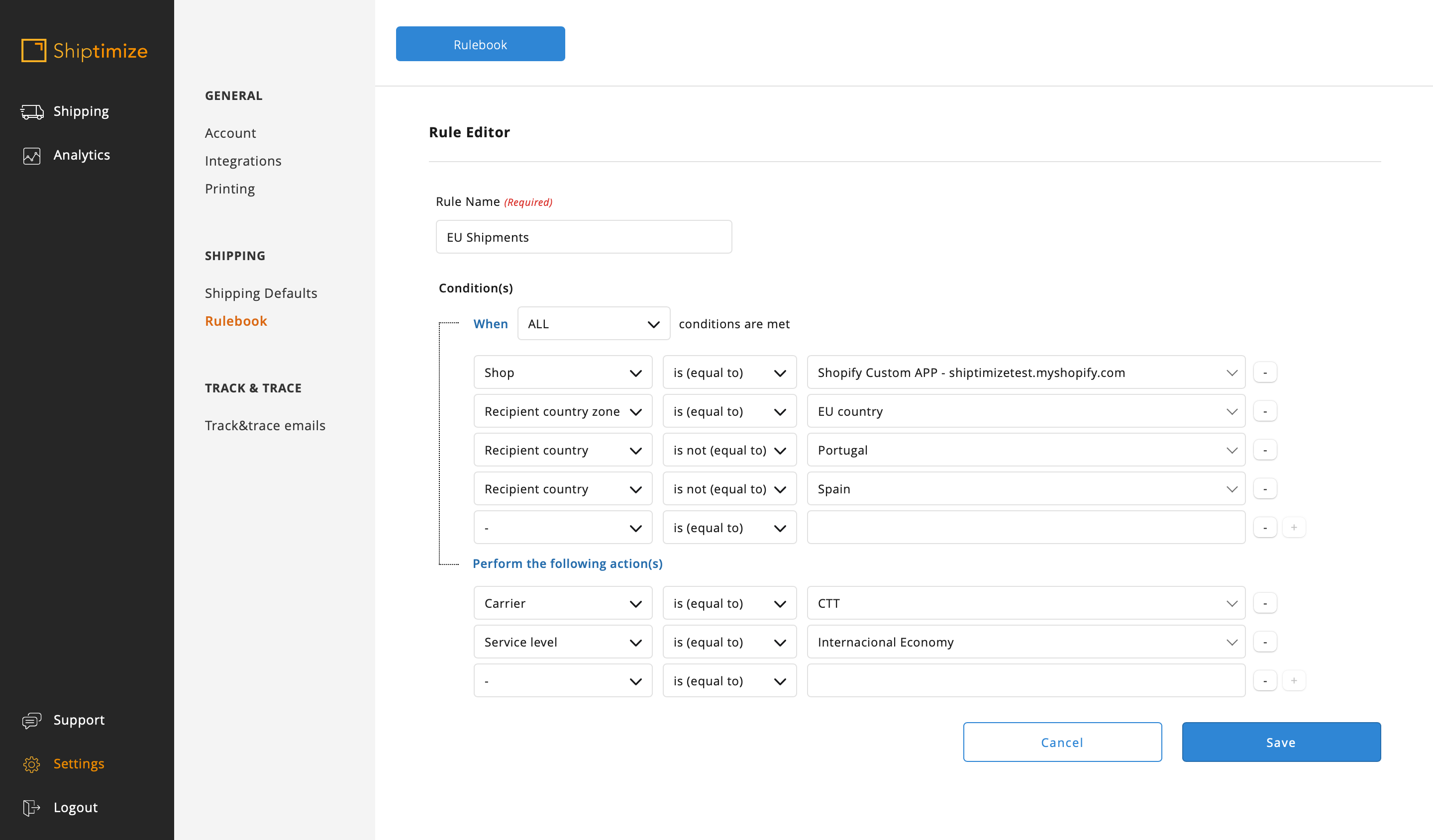
Or we add more conditions on the EU rule so as to exclude (not equal) Portugal and Spain
Open Source example rules
In the case of Open Source shops, the use of the rulebook avoids changing the settings already existing in the shipping methods in the online shop, but is more limited than the configuration of shipping rules using the shipping methods that appear in the online shop when installing the plugin CTT.
The rules created in this situation can be based on the whole shipping method name or on words that these names contain in case there are several shipping methods created in the shop or they can be based on other characteristics such as the country or zone of the destination country for example similar to what was previously indicated for the Closed Source shops.